Diabetes Management
How To Prevent Diabetes During Pregancy?
6 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 22 August 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
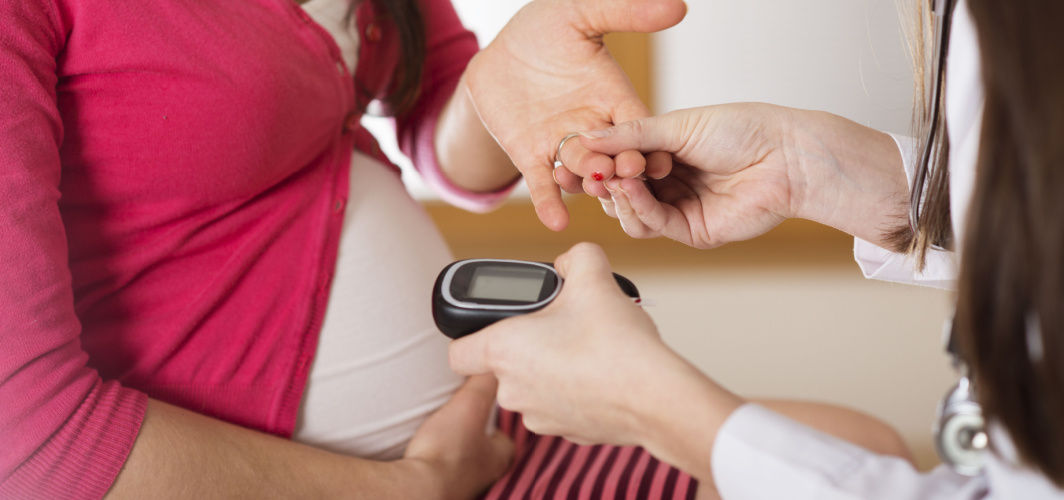

Gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, can have serious health implications for both the mother and baby. It is characterised by high blood sugar levels and can pose risks to both the mother and baby. Gestational diabetes occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels during pregnancy. This can lead to complications such as high birth weight, preterm birth and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. This article provides valuable information on how to prevent gestational diabetes and maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Although the exact cause of gestational diabetes is still unknown, several risk factors have been identified. By understanding these risk factors, you can take steps to prevent or manage gestational diabetes effectively.
1. Pre-Existing Factors
The following pre-existing factors play a significant role in determining the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes:
- A history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- A family history of diabetes, especially in your immediate family
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Obesity or excessive weight gain before pregnancy
2. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors that play a crucial role in gestational diabetes include:
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy diet high in processed foods and sugary beverages
- Excessive weight gain during pregnancy
- Age (women above 25 years are at higher risk)
Tips to Prevent Gestational Diabetes
Some basic tips to prevent gestational diabetes include:
1. Well-Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients for the proper growth and development of the foetus while preventing gestational diabetes. For a healthy diet, the below macronutrients play a vital role:
- Carbohydrates: Consume complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
- Proteins: Good sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
- Good fats: Healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados and olive oil, are crucial for the baby's brain development.
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals are equally important. Folic acid is essential for preventing neural tube defects and can be found in leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits and fortified cereals. Iron is needed to prevent anaemia and can be obtained from lean meats, beans, spinach and fortified grains.
2. Avoiding Certain Foods
Avoiding certain foods that can increase the risk of gestational diabetes during pregnancy is crucial. Here are some foods that should be avoided:
- Sugary drinks and snacks: These can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of gestational diabetes.
- Processed and fried foods: These foods are often high in unhealthy fats and sodium, which can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of gestational diabetes.
- High-sodium foods: Consuming excessive amounts of salt during pregnancy can lead to high blood pressure.
3. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in safe exercises, after consulting with your healthcare provider, can provide numerous benefits. Some suitable exercises for pregnant women include:
- Walking
- Prenatal yoga
- Swimming
- Stationary cycling
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine is crucial. Here are some tips to help you stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle:
- Engage in moderate-intensity activities: Activities like brisk walking, swimming or prenatal yoga are excellent options for staying active during pregnancy. They help improve cardiovascular health, increase muscle strength and reduce the risk of gestational diabetes.
- Schedule regular exercise sessions: Set aside specific times for exercise and make it a priority. Remember consistency is key.
- Set achievable goals: Start with small goals and gradually increase intensity and duration as your fitness level improves.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body feels during exercise. If you experience any discomfort or pain, modify or stop the activity.
4. Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups and medical care during pregnancy are crucial for the management of gestational diabetes. It is important to have regular visits with your healthcare provider to monitor blood sugar levels and overall health.
During these visits, your healthcare provider will monitor your
- Blood sugar levels to ensure they are within a healthy range.
- Weight, as excessive weight gain can contribute to gestational diabetes.
- Blood pressure and urine protein levels, to ensure both you and your baby are healthy throughout the pregnancy.
If you're at risk of developing gestational diabetes, your doctor may recommend a glucose tolerance test. The Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) is a common screening test used to detect gestational diabetes early in pregnancy by determining how your body processes sugar. The process involves:
- During the GTT, you will be asked to drink a sugary solution, typically containing 75 g of glucose.
- After consuming the solution, your blood sugar levels will be measured at regular intervals over 2 hours.
- This test helps determine how effectively your body metabolises glucose and identifies any potential issues with insulin regulation.
5. Stress Reduction in Gestational Diabetes
Pregnancy brings significant hormonal changes, which can make a woman experience a range of emotions, including stress, anxiety and frustration. Managing stress is crucial for overall well-being during pregnancy, especially when dealing with gestational diabetes. Here are some stress reduction techniques that you can incorporate into your daily routine:
- Practise relaxation exercises like deep breathing, meditation or guided imagery, which help calm the mind and reduce anxiety.
- Engage in activities that promote emotional well-being, such as reading a book, listening to soothing music or pursuing a hobby.
- Get regular exercise. Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters.
- Prioritise self-care by making time for activities you enjoy and finding ways to relax and unwind.
Summary
Preventing gestational diabetes during pregnancy is crucial for the well-being of both mother and baby. By emphasising the importance of preventive measures such as having a balanced diet, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight, women can significantly reduce their risk of developing gestational diabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels during pregnancy and seeking prenatal care is essential for early detection and management of gestational diabetes.
If you wish to know your risk of developing diabetes during pregnancy,
FAQs
Q. Can I prevent gestational diabetes through diet alone?
Although maintaining a balanced diet is crucial in preventing gestational diabetes, it may not be the only factor. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight and monitoring blood sugar levels are equally important.
Q. How often should I exercise during pregnancy to prevent gestational diabetes?
It is recommended to engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 30 minutes. However, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen during pregnancy.
Q. Can gestational diabetes be prevented if I am already overweight?
By adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes.
Q. Is it necessary to monitor blood sugar during pregnancy if I have no symptoms?
Even if you do not experience any symptoms of gestational diabetes, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to detect any potential abnormalities to prevent any complications for both the mother and baby.
Q. Can breastfeeding help prevent diabetes after gestational diabetes?
Yes, breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes for both the mother and child.
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Stress and Kidney Disease: Is There a Relationship?
In a recent study, scientists concluded that stress-related disorders can increase the risk of developing acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.

Diabetes Management
Can Diabetics Eat Bananas?
Diabetics can eat bananas but in moderation. Bananas are a good source of fibre, potassium, and vitamins. However, bananas also contain natural sugars, so portion control is important. It's recommended to choose ripe bananas with a lower glycemic index and include them as part of a balanced meal or snack.
Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Stress and Kidney Disease: Is There a Relationship?
In a recent study, scientists concluded that stress-related disorders can increase the risk of developing acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.

Diabetes Management
Can Diabetics Eat Bananas?
Diabetics can eat bananas but in moderation. Bananas are a good source of fibre, potassium, and vitamins. However, bananas also contain natural sugars, so portion control is important. It's recommended to choose ripe bananas with a lower glycemic index and include them as part of a balanced meal or snack.

Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.