Orthopedic Conditions
Could a Slipped Disc Be Causing That Sudden Back Pain?
5 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 15 June 2021, Updated on - 18 October 2022
Share this article
0
10 likes

A slipped disc occurs when a soft cushion of tissue between the bones in the spine pushes out, causing discomfort and pain. These soft tissues or rubbery discs that cushion the spinal bones provide stability, flexibility, and mobility to the spine when lifting, twisting, or bending. However, excessive strain, an injury, or natural wear and tear can cause a rupture in a spinal disc, causing a slipped disc. It often occurs in the lower back and is one of the most common causes of back pain in adults. Although painful, a slipped disc usually heals on its own over time or may only require physical therapy. It is also possible to prevent a disc rupture and back pain by making simple lifestyle changes.
Understanding more about spinal discs and the cause of slipped discs
Spinal discs are soft rubbery pads positioned between the vertebrae, the small bones that make the spinal column (backbone). Spinal discs are the most critical structures in the spine. They cushion the vertebrae, absorb shock and stress, and allow flexible movements in the spine. A spinal disc comprises a tough, fibrous outer ring and an inner soft gel-like material. When a disc ruptures, the soft inner material herniates (pushes out) between the vertebrae. The herniated disc tissue can compress the nerves in the surrounding area and irritate them, causing significant pain.
The wear and tear of spinal discs which occurs as a part of the usual ageing process are the cause of the slipped discs in the majority of people. Though rare, slipped discs can also occur due to damage of a spinal disc caused by an accident or serious injury.
A disc rupture can happen in any part of the spine but the most frequent areas affected are the lower back and neck. Depending upon the location of the slipped disc, it causes pain in the back or neck, leg, or arm, and the pain may be accompanied by weakness and numbness.
Symptoms of slipped discs
There may be no symptoms at all if the slipped disc is not pressing on the nerve. However, if the nerves are involved, the symptoms include:
- Lower back pain or neck pain, depending on the location of the slipped disc
- Slipped disc in the lower back causes pain in the hips, buttocks, or legs
- Slipped disc in the neck causes pain in the shoulder and arm
- Dull ache on one side of the body
- Difficulty bending or straightening the back
- Muscle weakness, reduced ability to lift and hold objects, or walk properly
- Numbness or tingling sensation in the shoulders, arms, hands, back, legs, or feet
- Movements like coughing and sneezing can cause sharp or burning pain that shoots into the arm or leg, and can also induce sudden bouts of pain
- Sharp or burning pain that shoots into the arm or leg when coughing or sneezing. These movements can also induce sudden bouts of pain.
How to know if the back pain is associated with a slipped disc
There can be many causes of back pain, but pain that radiates down the leg and into the foot may be a possible sign of a slipped disc. If the neck area is affected, the pain may radiate into the arms. This is because the slipped disc presses on the nerves that exit the spine leading to pain and other symptoms along the nerve pathway. A medical examination will be the best way to identify a slipped disc situation.
Risk factors of slipped discs
Slipped disc mainly occurs in individuals between 30 and 50 years of age, and men are more likely to be affected. The factors involved include:
- Ageing, associated with degeneration and weakening of the disc due to wear and tear, and shrinkage due to water loss
- Excessive strain related to strenuous exercise
- Improper lifting of heavy objects using back muscles, instead of thigh and leg muscles
- Sudden twisting and turning of the spine
- Being physically inactive that causes weakening of back and abdominal muscles that support the spine
- Being overweight, as excess weight strains the back
- Frequent driving which involves prolonged sitting
- Vibrations from the vehicle engine or operating machinery that can put pressure on the spinal discs
- Smoking, which is linked to a decrease in oxygen supply to the spinal discs accelerating the degenerative process.
Diagnosing slipped disc
It is essential to rule out other causes of similar pain like fractures, infections, or tumours. The doctor usually diagnoses slipped disc based on the symptoms and physical examination. A neurological examination may also be performed to check the muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation. Other tests may include imaging tests like Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans to know the exact size and location of the slipped disc, and the affected nerves. Nerve tests may also be conducted to assess the function of muscles and nerves and to detect damage to these.
Treatment of slipped disc
The symptoms of a slipped disc usually go away on their own in less than six weeks. If symptoms persist, conservative treatment is recommended that includes adequate rest, proper nutrition, medications, and physical therapy. In addition to medications, applying a heating pad or ice pack to the affected area, avoiding long periods of bed rest, and resuming activities gradually can help manage the condition.
Physiotherapy plays a significant role in treating slipped discs. Some of the prominent treatments for a herniated disc include light exercises, soft tissue massage, and acupuncture. If these measures fail, spinal injections or surgery may be required.
Conclusion
As slipped discs occur over time due to improper postures or lifting techniques, it is essential to know how the spine gets impacted by daily activities. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, regular exercise, and stretching can go a long way in preventing slipped discs. However, the majority of people (around 90%) with a slipped disc recover and return to normal activities without surgical treatment. The lower back pain associated with the condition can be effectively relieved with an exercise regimen to stretch and strengthen the back.
For any questions on musculoskeletal health including slipped discs, you can talk to an orthopaedician.
Orthopedic Conditions
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Orthopedic Conditions
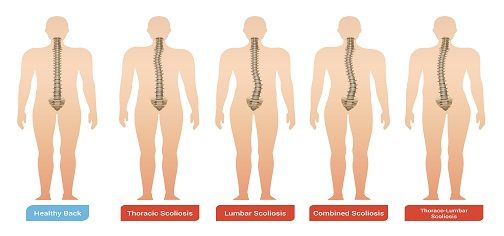
5 Facts About Scoliosis Every Parent Should Know
Scoliosis is the most prevalent among children and adolescents, usually occurring in children aged 10 to 15. While most scoliosis cases are mild, the condition can worsen and lead to respiratory issues.

Orthopedic Conditions
Sharp pain in the heel? These could be the reasons!
Heel pain can occur due to stress or injury. However, it can be treated easily with the help of medical appliances, comfortable footwear, physical therapy, and medication.
Orthopedic Conditions
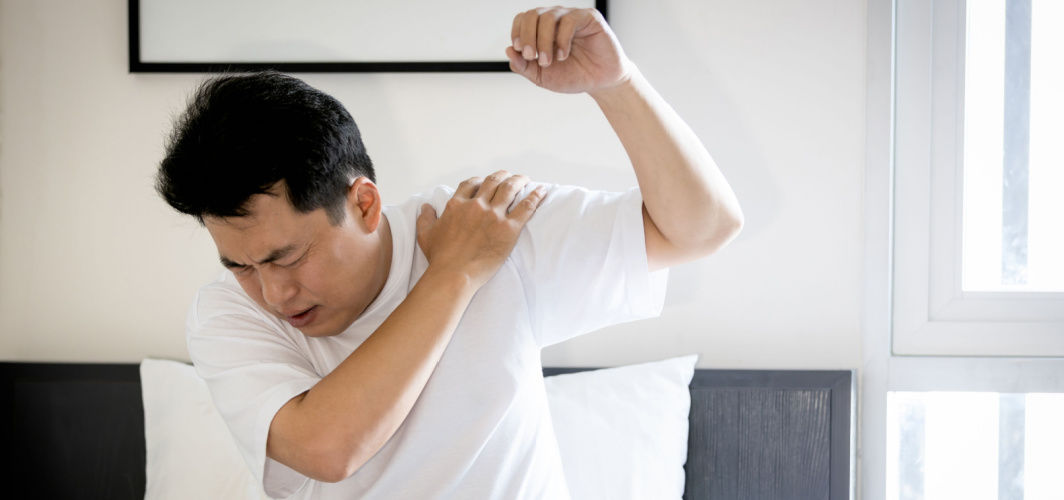
Frozen Shoulder: Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a frozen shoulder. Learn how to manage this condition and regain full control of your shoulder.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

10 Foods That Are Unhealthy for Your Bones
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Orthopedic Conditions
5 Facts About Scoliosis Every Parent Should Know
Scoliosis is the most prevalent among children and adolescents, usually occurring in children aged 10 to 15. While most scoliosis cases are mild, the condition can worsen and lead to respiratory issues.

Orthopedic Conditions
Sharp pain in the heel? These could be the reasons!
Heel pain can occur due to stress or injury. However, it can be treated easily with the help of medical appliances, comfortable footwear, physical therapy, and medication.

Orthopedic Conditions
Frozen Shoulder: Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a frozen shoulder. Learn how to manage this condition and regain full control of your shoulder.