Diabetes Management
Five Essential Tips for Diabetes Self-Management
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 05 October 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
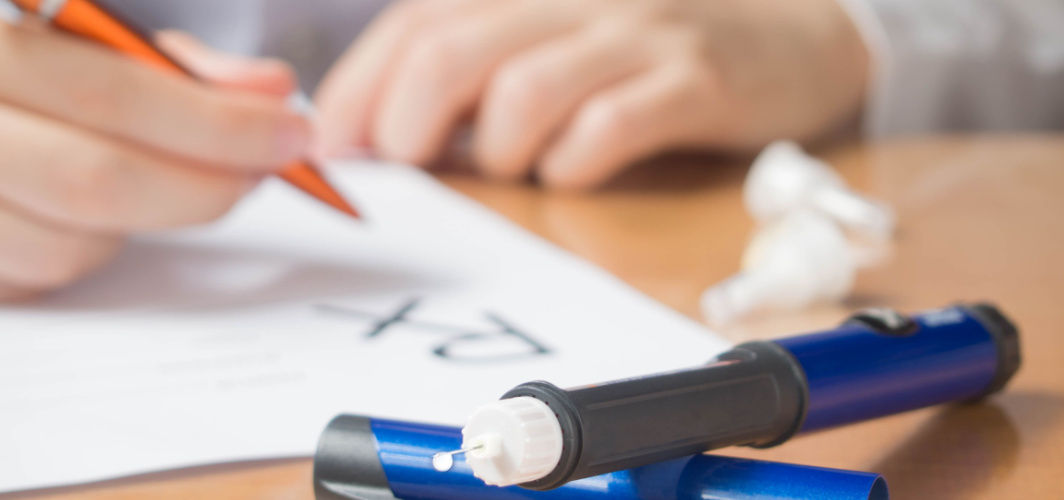

Diabetes, a chronic condition characterised by high blood sugar levels, requires diligent self-management to maintain optimal health and prevent complications. Whether you have Type 1, Type 2, or Gestational Diabetes, here are five crucial tips to help you take control of your diabetes and lead a healthier life.
1. Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of diabetes self-management. Use a glucometer to check your blood sugar levels regularly, especially before and after meals, and keep a log of your readings. Understanding how your body responds to different factors like food, exercise, and medications empowers you to make informed decisions about your diabetes care.
2. Balanced Diet and Portion Control
A balanced diet is vital for managing diabetes effectively. Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Practice portion control to avoid overeating, and pay attention to carbohydrate intake, as it directly affects blood sugar levels. Consult with a registered dietitian to create a personalised meal plan that aligns with your specific dietary needs and preferences.
3. Regular Physical Activity
Exercise plays a significant role in diabetes management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with strength training exercises on two or more days. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, control weight, and boost overall well-being. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program.
4. Medication Adherence
Adhere to your treatment plan diligently if you have been prescribed medication for your diabetes management. Take medications as directed by your healthcare provider and at the recommended times. Missing doses or altering your medication regimen without consulting your doctor can lead to unstable blood sugar levels.
5. Stress Management and Self-Care
Stress can impact blood sugar levels, so it's essential to practise stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or hobbies that help you relax. Prioritise self-care and ensure you get enough sleep, as quality rest contributes to better blood sugar control. Don't hesitate to seek support from healthcare professionals or mental health experts if you're struggling with stress or emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively involves being proactive so that you can keep your condition under control.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Useful Tips for Diabetics Taking up Long-distance Running
Before running, check blood sugar levels and adjust carbohydrate intake accordingly. Carry glucose tablets or energy gels for energy and glucose boosts. Stay hydrated by drinking small amounts frequently during the run. It's helpful to have a running companion for first-aid support in case of low blood sugar. Carry medical ID or contact details for emergencies.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.
Diabetes Management
7 Reasons Why Blood Sugar Logging is Important in Diabetes?
Blood sugar logging is vital for managing diabetes effectively. It offers insights into glycemic control, aids in treatment adjustments, and prevents hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Additionally, it guides lifestyle modifications, helps prevent long-term complications, enables personalised diabetes management, and provides a sense of control and peace of mind. By actively monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes care, reduce risks, and lead healthier lives with diabetes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Useful Tips for Diabetics Taking up Long-distance Running
Before running, check blood sugar levels and adjust carbohydrate intake accordingly. Carry glucose tablets or energy gels for energy and glucose boosts. Stay hydrated by drinking small amounts frequently during the run. It's helpful to have a running companion for first-aid support in case of low blood sugar. Carry medical ID or contact details for emergencies.

Diabetes Management
Eating Out in Festivals: Tips for a Healthier Dining Experience
Dining out with diabetes can still be a delightful experience with some careful choices. To enjoy restaurant meals while managing your blood sugar levels, plan ahead by reviewing the menu and choosing dishes wisely, focusing on lean proteins and vegetables. Watch portion sizes and control carbohydrates. Request dressings and sauces on the side and opt for healthier beverage choices. Be mindful of desserts and share them if needed. Communicate your dietary needs with the person who is serving, and try to stick to your regular meal schedule for stable blood sugar levels. Dining out can be a pleasure with these strategies in mind.

Diabetes Management
7 Reasons Why Blood Sugar Logging is Important in Diabetes?
Blood sugar logging is vital for managing diabetes effectively. It offers insights into glycemic control, aids in treatment adjustments, and prevents hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Additionally, it guides lifestyle modifications, helps prevent long-term complications, enables personalised diabetes management, and provides a sense of control and peace of mind. By actively monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diabetes care, reduce risks, and lead healthier lives with diabetes.