General Health
Flu Shot: How It Works And Why Should You Get It?
8 min read
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on - 29 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
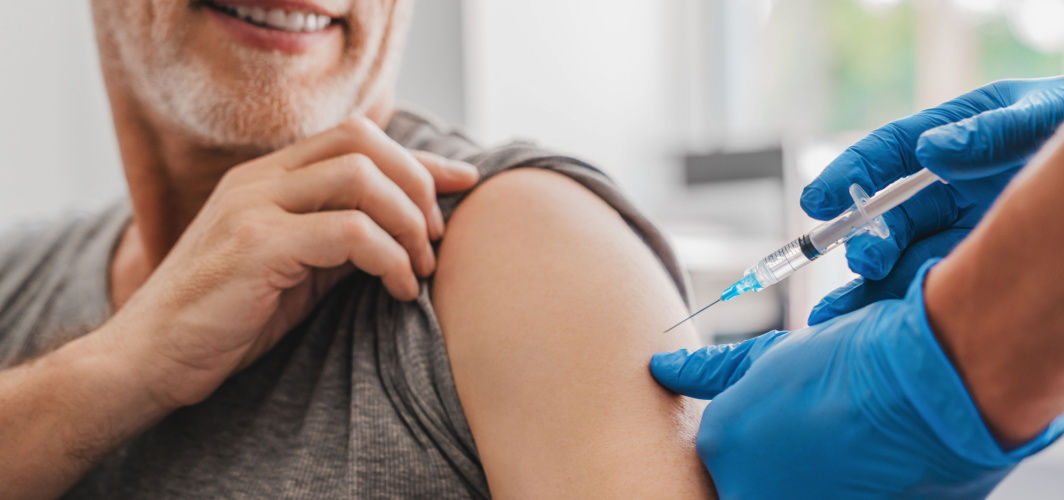
Flu, or influenza, is a highly contagious viral infection that affects the respiratory system. It can cause mild to severe illness and can even be life-threatening in certain cases. Influenza viruses are constantly evolving, which makes it necessary to get vaccinated annually. The flu vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of the virus and protect yourself and others from getting sick. Let's know more about it in this blog.
What is the Flu Shot?
The flu shot, also known as the influenza vaccine, provides protection against the flu virus. The flu shot works by stimulating your immune system to produce antibodies against specific strains of the flu virus. These antibodies help your body recognise and fight off the virus if you are exposed to it later on. The flu shot is typically given through an injection, either in the arm or thigh.
Composition and Effectiveness of the Vaccine
The composition of the flu shot changes every year to match the most prevalent strains of the flu virus. Each year, experts from around the world gather data on which strains are circulating and make predictions on which strains are most likely to be widespread during the upcoming flu season. Based on this information, they select the strains that will be included in the vaccine.
The effectiveness of the flu shot can vary from year to year depending on how well it matches the circulating strains of the virus. On average, the flu shot reduces the risk of getting sick by about 40-60%. Even if you do get infected with a strain not covered by the vaccine, it can still help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
How Does The Flu Shot Work?
To understand how the flu shot works, we first need to understand the role of antibodies in our immune system. This is how a flu shot works:
- Antibodies are proteins produced by our immune cells, specifically B-cells, in response to foreign substances, such as viruses or bacteria. These antibodies play a crucial role in neutralising and eliminating these invaders from our body.
- When we receive a flu shot, it contains inactivated or weakened forms of the flu virus strains that are expected to circulate during the upcoming flu season.
- Once injected into our body, our immune system recognises these viral components as foreign and mounts an immune response. This response includes the activation of B-cells, which produce specific antibodies that recognise and target the flu virus.
- One of the remarkable features of our immune system is its ability to form memory cells. These cells "remember" specific pathogens they have encountered before and enable a rapid and efficient response when exposed to them again.
- After receiving a flu shot, some of the B-cells that produce flu-specific antibodies transform into memory B-cells. These memory B-cells "store" information about the flu virus strains encountered in the vaccine. If we are exposed to those strains in the future, these memory B-cells quickly reactivate and produce antibodies to fight off the infection.
- By receiving a flu shot, we essentially prime our immune system to recognize and respond effectively to the specific strains of flu virus found in the vaccine. This allows our body to mount a quicker and stronger defence when exposed to the actual flu virus strains in the future.
Who Should Get The Flu Shot?
Influenza vaccination, commonly known as the flu shot, is recommended for various age groups and individuals with certain health conditions. Getting vaccinated not only protects you from the flu but also helps prevent the spread of the virus to others. Let's take a closer look at who should consider getting the flu shot.
1. Children and infants
- Children are often more vulnerable to complications from the flu due to their developing immune systems.
- Vaccinating children can help reduce the risk of severe illness and hospitalisation.
2. Adults, including pregnant women
- Pregnant women are at an increased risk of severe illness from the flu and have a higher chance of complications such as premature labour.
- The flu shot is safe for pregnant women and protects both the mother and the baby.
3. Older adults
- As we age, our immune system weakens, making older adults more susceptible to severe complications from the flu.
- Flu vaccination can help lower the risk of hospitalisation and death among older adults.
- Elderly individuals need to receive the flu shot annually to maintain their health and well-being.
4. People with chronic conditions
- Individuals with chronic health conditions, such as asthma, diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease, are at a higher risk of developing severe complications from the flu.
- Vaccination is crucial for these individuals since it can reduce their chances of hospitalisation or other serious health issues related to the flu.
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatment or organ transplantation, should also receive the flu shot to protect themselves from respiratory infections.
When And Where To Get A Flu Shot In India?
In India, flu season typically occurs during the monsoon and winter months, with cases peaking between July and March. However, it's important to note that the timing and severity of the flu season can vary from year to year.
In India, flu vaccines are readily available and can be obtained from various sources such as:
- Hospitals and clinics
- Pharmacies
- Government health centres
- Corporate health programs
- Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and community health centres
Benefits Of Getting A Flu Shot
There are several benefits of getting a flu shot:
- Studies have shown that getting a flu shot can significantly reduce the risk of hospitalisations due to influenza-related complications.
- It can reduce the risk of developing serious complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus infections, which can arise from the flu.
- The vaccine can also lower the mortality rates associated with the flu, especially among high-risk populations.
- Healthcare workers are at an increased risk of exposure to the flu virus due to their proximity to patients who may be infected. Getting vaccinated not only protects them from contracting the flu but also prevents the spread to vulnerable patients.
- Older adults, young children, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic health conditions are more susceptible to severe illness from the flu. Vaccination helps provide them with an extra layer of protection.
Tips For A Healthy Lifestyle During Flu Season
Measures that may help prevent flu include:
- Handwashing: Regularly wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially before eating, after using the restroom, and after coughing or sneezing.
- Respiratory etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets. Dispose of used tissues immediately and wash your hands afterwards.
- Avoid close contact: Try to avoid close contact with individuals who are sick, as well as crowded places where the risk of exposure may be higher.
- Nutritious diet: Ensure that you consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support immune function.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration helps in flushing out toxins from the body and facilitates a better immune response. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost circulation and enhance immune function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise at least 5 days of the week.
- Prioritise sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to support your body's immune functions.
- Stress management: Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Conclusion
Getting vaccinated against the flu is crucial for maintaining good health. The flu vaccine not only protects against the influenza virus but also helps prevent the spread of the virus to others. Make an appointment with your healthcare provider or visit a nearby vaccination centre to get your flu shot.
FAQs
Q. How does the flu shot work to protect against different strains of the flu virus?
The flu shot is designed to stimulate your immune system to produce antibodies specific to the strains of the flu virus included in the vaccine. These antibodies help your body recognise and fight off the virus if you're exposed to it.
Q. Why is it important to get a flu shot every year?
The flu virus can mutate and change rapidly, leading to new strains each year. To stay effective, the flu shot is updated annually to include the most likely strains to circulate during the upcoming flu season.
Q. Are there any side effects of getting a flu shot?
Common side effects include soreness at the injection site and mild flu-like symptoms such as low-grade fever and fatigue, and serious side effects are extremely rare.
Q. Who should get a flu shot?
While the flu shot is generally recommended for most individuals, certain groups, such as the elderly, young children, pregnant women, and those with certain medical conditions, are especially encouraged to get vaccinated.
Q. Can the flu shot provide complete immunity against the flu virus?
No, the flu shot does not offer complete immunity against the flu virus. It is designed to reduce the risk of getting the flu and its severity. The effectiveness of the vaccine can vary from year to year depending on how well it matches the circulating flu strains.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
Azithromycin Tablets: Benefits, Side Effects, Dosage
Azithromycin is a common medicine used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections. It works by inhibiting bacterial growth and should be used as healthcare providers prescribe. This article discusses precautions, proper usage, and potential side effects to ensure safe and effective use.

General Health
Do Your Eyes Feel Fatigued? Following These Tips Can Help!
Our eyes often get dry and fatigued by staring at the screens of computers, phones, or tablets for extended periods of time. The 20-20-20 rule can be used to assist in combating this issue.

General Health
What Are The Symptoms Of Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D is important for a healthy functioning of the body. Discover effective preventative methods, like sun exposure, dietary changes, and supplements that can help prevent vitamin D deficiency. This blog is a guide to help you know about vitamin D deficiency symptoms, causes and more.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Science-backed Home Remedies for Burns and Blisters
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Azithromycin Tablets: Benefits, Side Effects, Dosage
Azithromycin is a common medicine used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections. It works by inhibiting bacterial growth and should be used as healthcare providers prescribe. This article discusses precautions, proper usage, and potential side effects to ensure safe and effective use.

General Health
Do Your Eyes Feel Fatigued? Following These Tips Can Help!
Our eyes often get dry and fatigued by staring at the screens of computers, phones, or tablets for extended periods of time. The 20-20-20 rule can be used to assist in combating this issue.

General Health
What Are The Symptoms Of Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D is important for a healthy functioning of the body. Discover effective preventative methods, like sun exposure, dietary changes, and supplements that can help prevent vitamin D deficiency. This blog is a guide to help you know about vitamin D deficiency symptoms, causes and more.