General Health
How to Reduce Body Heat: Expert Tips for Managing Hyperthermia
6 min read
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on - 24 August 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
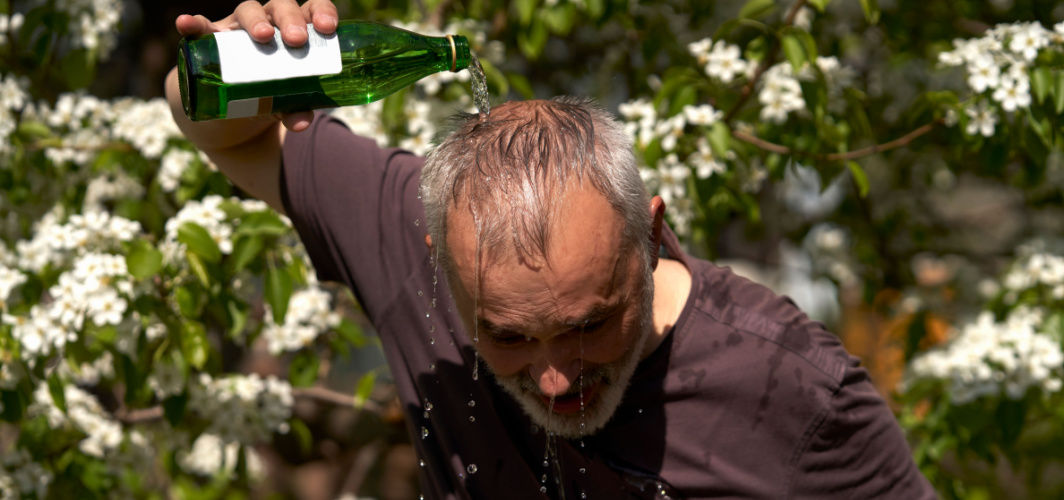

Body heat is the internal temperature that is maintained by our bodies. It is crucial for various bodily functions, such as metabolism, enzymatic reactions, and nerve signaling. Our body thermoregulates to maintain this heat within a narrow range of 36.5-37.5 degrees Celsius. Hyperthermia, on the other hand, occurs when our body's heat regulation system fails, resulting in an abnormally high internal temperature. Maintaining a balanced body temperature is crucial for overall health and well-being. Excessive heat can put a strain on the body's organs and systems, leading to various health problems.
Why Body Heat Regulation Matters
Let's understand why body heat regulation is crucial:
The Role of Thermoregulation in the Body
- The human body continuously works to maintain a stable internal environment, regardless of external conditions. One of the critical processes involved in this regulation is thermoregulation, which refers to the body's ability to maintain an optimal internal temperature.
- Our body has several natural cooling mechanisms that come into play when we are exposed to heat. These mechanisms include sweating, which helps dissipate heat through evaporation, and vasodilation, where the blood vessels near the skin surface widen, allowing heat to escape more efficiently.
- Excessive heat can result in dehydration, heat exhaustion, or even heatstroke, while prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can cause hypothermia.
Factors Contributing to Increased Body Heat
- External factors: Hot weather, physical activity, and exposure to hot environments can significantly impact body temperature. During hot weather or intense physical activities, our body produces more heat than usual, requiring efficient cooling mechanisms to maintain an optimal temperature.
- Internal factors: Fever, certain medical conditions like hyperthyroidism or infections, and medications can also affect body heat regulation.
Lifestyle Modifications for Reducing Body Heat
One can aid their body's mechanism of maintaining its heat by the following methods:
1. Hydration for Optimal Cooling
When we sweat, our body loses fluids that need replacing. Adequate hydration ensures that our body can produce sweat effectively and regulate its temperature. Here are some tips for optimal hydration:
- Drink water regularly throughout the day, even if you do not feel thirsty. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Include hydrating foods in your diet, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and citrus fruits.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugary drinks and caffeine, as they can dehydrate the body.
2. Appropriate Clothing Choices
Choosing breathable fabrics and loose-fitting clothing allows better air circulation and helps in dissipating heat from our bodies. Consider these tips for selecting suitable clothing during hot weather or physical activities:
- Choose fabrics like cotton or linen to allow air to circulate your body, promoting better ventilation.
- Wear light-colored clothing - it reflects sunlight and reduces heat absorption.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothes or synthetic materials that trap heat and hinder the evaporation of sweat.
3. Cooling Techniques for Immediate Relief
Taking a cold shower or bath is an effective way to lower your body temperature quickly.
The application of cool compresses or ice packs on pulse points such as below can help bring down body temperature rapidly.
- Wrists
- Neck
- Temples
- The back of your knees
Dietary Strategies for Managing Body Heat
1. Foods That Help Cool the Body
Certain foods possess cooling properties that can help regulate body temperature including:
- Watermelon: This hydrating fruit is not only delicious but also helps in cooling down the body due to its high water content.
- Cucumber: Known for its high water content, cucumber aids in keeping the body hydrated and contributes to reducing body heat.
- Mint: Adding mint leaves to your meals or drinking mint-infused water can have a cooling effect on the body.
2. Avoiding Foods That Increase Body Heat
Some foods can increase body heat and should be consumed in moderation, especially during hot weather. These include:
- Spices like chili peppers and ginger can raise body temperature and induce sweating.
- Alcohol may give you a temporary sensation of warmth. However, it actually dilates blood vessels and increases heat loss, making it harder for your body to regulate temperature.
3. Hydrating and Cooling Beverages
Staying hydrated is crucial for managing body heat. Opt for chilled and hydrating beverages that can help cool down your body. Some examples include:
- Coconut water: A natural source of electrolytes, coconut water helps in maintaining hydration levels.
- Mint-infused water: Adding fresh mint leaves to water provides a refreshing and cooling drink.
- Herbal teas: Chamomile and peppermint teas have cooling properties and can be enjoyed hot or chilled.
It is important to avoid sugary drinks and caffeine as they can lead to dehydration and increase body heat.
Natural Remedies to Reduce Body Heat
When it comes to reducing body heat, there are several natural remedies backed by science that can help regulate your internal temperature.
1. Herbal Infusions and Teas
Herbs with cooling properties can be highly effective in reducing body heat, such as:
- Peppermint: Known for its refreshing taste and cooling effect, peppermint tea can help lower your body temperature.
- Chamomile: Apart from its calming properties, chamomile tea has a cooling effect on the body and can help reduce heat.
2. Ayurvedic Practices for Balancing Pitta Dosha
According to Ayurveda, an ancient Indian system of medicine, balancing the Pitta dosha is key to managing body heat. Pitta dosha represents the fire element in our bodies, and an imbalance in this dosha can lead to excessive body heat. Here are some Ayurvedic recommendations for managing Pitta dosha and reducing body heat:
- Herbal Supplements: Ayurvedic herbs like Amla (Indian Gooseberry), Brahmi, and Neem can help balance Pitta dosha and cool down the body.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation and yoga, as stress can increase Pitta dosha.
Managing Body Heat in Specific Situations
Body heat can also increase in some specific situations.
1. Exercising Safely in Hot Weather
- Avoid exercising during the hottest parts of the day, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Take frequent breaks in shaded areas to cool down.
- Listen to your body and modify your exercise intensity or duration as needed.
- Take advantage of air-conditioned spaces, such as gyms or indoor tracks, if available.
- If possible, choose water-based activities like swimming or water aerobics, which can help regulate body temperature more effectively.
2. Coping with Menopausal Hot Flashes
Menopause is a natural phase of a woman's life, but the accompanying hot flashes can be uncomfortable and disruptive.
- Dress in layers, so you can easily remove clothing when you feel a hot flash coming on.
- Avoid triggers such as spicy foods, hot beverages, alcohol, and caffeine, which can exacerbate hot flashes.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing exercises, yoga
- In more severe cases, hormone therapy may be necessary to effectively manage hot flashes.
Conclusion
Understanding how to manage and reduce body heat is essential for maintaining overall well-being. The expert tips provided in this blog offer practical guidance for dealing with hyperthermia and staying comfortable in hot conditions. By following these recommendations, you can take proactive steps to stay cool, hydrated, and healthy.
FAQs
Q1. Can emotional stress increase body heat?
A1. Yes, it can.
Q2: What causes body heat?
A2: Body heat is primarily caused by metabolic processes in your body. When your cells work to carry out various functions, they generate heat as a byproduct.
Q3. What are the symptoms of excessive body heat?
A3. Excessive sweating, flushed skin, rapid heartbeat, headaches, dizziness or lightheadedness.
Q4. How is body heat measured?
A4. Using a thermometer to measure oral temperature, by placing the thermometer under the tongue, measuring temperature in the ear (tympanic), forehead (temporal), or armpit (axillary) are some ways to measure body heat.
Q5. What is considered a normal body temperature?
A5. A temperature between 97°F (36.1°C) and 99°F (37.2°C) is generally considered normal.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

General Health
Cataract: Recognizing the Early Signs
A cataract is a condition where the lens of the eye, which is usually clear, gets clouded, causing blurry or loss of vision. Most cataracts are related to ageing.
General Health
Varicose Veins: When to Worry About the Bluish Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged and prominent swollen veins that mostly occur on the body's lower half, mainly on the legs and feet. They may be purple or blue, often resembling spider veins that are smaller, milder, and less bulgy than varicose veins.

General Health
Chickenpox: Know The Treatment, Vaccine, & Complications
Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, chickenpox is characterised by a red, itchy rash with fluid-filled blisters that appear all over the body. Usually occurring in children, it is accompanied by symptoms like fever, fatigue, and headache. Here is more about chickenpox, its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Science-backed Home Remedies for Burns and Blisters
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Cataract: Recognizing the Early Signs
A cataract is a condition where the lens of the eye, which is usually clear, gets clouded, causing blurry or loss of vision. Most cataracts are related to ageing.

General Health
Varicose Veins: When to Worry About the Bluish Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged and prominent swollen veins that mostly occur on the body's lower half, mainly on the legs and feet. They may be purple or blue, often resembling spider veins that are smaller, milder, and less bulgy than varicose veins.

General Health
Chickenpox: Know The Treatment, Vaccine, & Complications
Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, chickenpox is characterised by a red, itchy rash with fluid-filled blisters that appear all over the body. Usually occurring in children, it is accompanied by symptoms like fever, fatigue, and headache. Here is more about chickenpox, its symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention.