Diabetes Management
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Is it Important?
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 13 September 2023, Updated on - 14 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
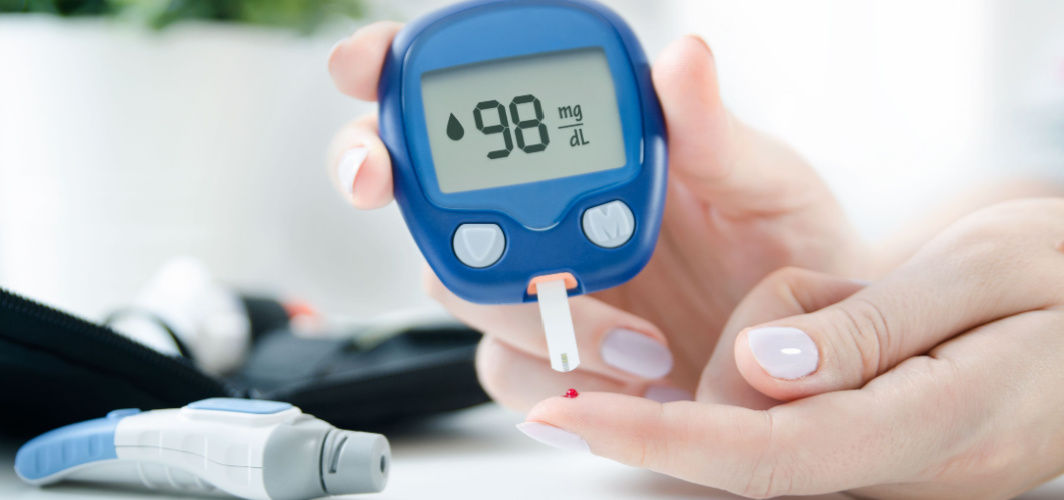
Blood sugar monitoring is a critical aspect of managing your health, especially if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing it. This practice involves regularly measuring your blood glucose levels to understand how your body processes sugar. In this blog, we'll delve into the significance of blood sugar monitoring, its impact on your overall well-being, and why it's vital to make it a part of your routine.
What is Blood Sugar?
Before we explore the importance of blood sugar monitoring, let's understand what blood sugar (glucose) is and why it matters. Glucose is a type of sugar that comes from the food we eat and serves as a primary energy source for our cells. However, too much or too little glucose in the bloodstream can lead to health issues.
Why Is Blood Sugar Monitoring Important?
Blood sugar monitoring is important for gaining insights about your overall health and to help you make informed decisions about your diet, medication and lifestyle choices.
- Personalized Management: Monitoring allows you to understand how your body responds to food, physical activity, medication, and other factors. This knowledge enables you and your healthcare provider to create a personalized diabetes management plan.
- Preventing Complications: High blood sugar levels over time can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and vision impairment. Monitoring helps you take timely action to prevent these issues.
- Adjusting Medication: If you're on diabetes medication, monitoring helps you and your healthcare provider determine if your current treatment plan is effective. Adjustments can be made if necessary to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle Modification: Blood sugar monitoring provides insights into the impact of your lifestyle choices. You can make informed decisions about your diet, exercise routine, and stress management to better control your blood sugar.
Quality of Life:
- Stable blood sugar levels contribute to an improved quality of life.
- You'll have more energy, experience fewer fluctuations in mood and energy, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications that can diminish your well-being.
Incorporating Blood Sugar Monitoring into Your Routine
To make blood sugar monitoring a seamless part of your life:
- Invest in a Glucometer: Purchase a reliable glucometer and test strips for at-home monitoring.
- Follow a Schedule: Work with your healthcare provider to establish a testing schedule that suits your needs.
- Record and Analyze Results: Keep a record of your blood sugar readings and share them with your healthcare team for better guidance.
Conclusion
Blood sugar monitoring is a powerful tool for taking control of your health. By regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels, you can detect issues early, personalize your management plan, prevent complications, and lead a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Celebrate Diwali While Keeping Your Blood Sugar In Control!
With these tips, you can enjoy the festival of Diwali while keeping a check on your blood sugar levels.

Diabetes Management
Can Regular Exercise Help Beat Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can be managed successfully with early detection and lifestyle changes. Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes must eat a healthy diet, stay physically active, regularly monitor blood glucose levels and follow their medications to manage gestational diabetes. They can also consult a dietitian for a balanced meal plan. Medications like metformin may be prescribed by doctors if needed.
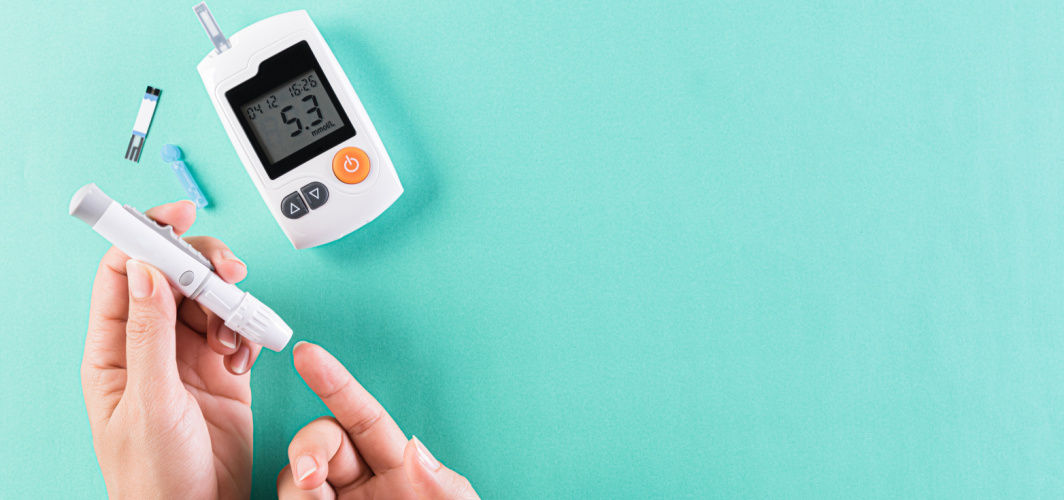

Diabetes Management
How Diabetes Can Affect Your Digestive System
Learn about the latest updates in guidelines, new technologies, and lifestyle factors to manage diabetes effectively. Discover valuable information on prevention, treatment, and living a healthy life with diabetes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Celebrate Diwali While Keeping Your Blood Sugar In Control!
With these tips, you can enjoy the festival of Diwali while keeping a check on your blood sugar levels.

Diabetes Management
Can Regular Exercise Help Beat Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes can be managed successfully with early detection and lifestyle changes. Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes must eat a healthy diet, stay physically active, regularly monitor blood glucose levels and follow their medications to manage gestational diabetes. They can also consult a dietitian for a balanced meal plan. Medications like metformin may be prescribed by doctors if needed.

Diabetes Management
How Diabetes Can Affect Your Digestive System
Learn about the latest updates in guidelines, new technologies, and lifestyle factors to manage diabetes effectively. Discover valuable information on prevention, treatment, and living a healthy life with diabetes.