General Health
Shingles Vaccine: All You Need To Know About Shingrix
7 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 30 August 2023, Updated on - 01 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
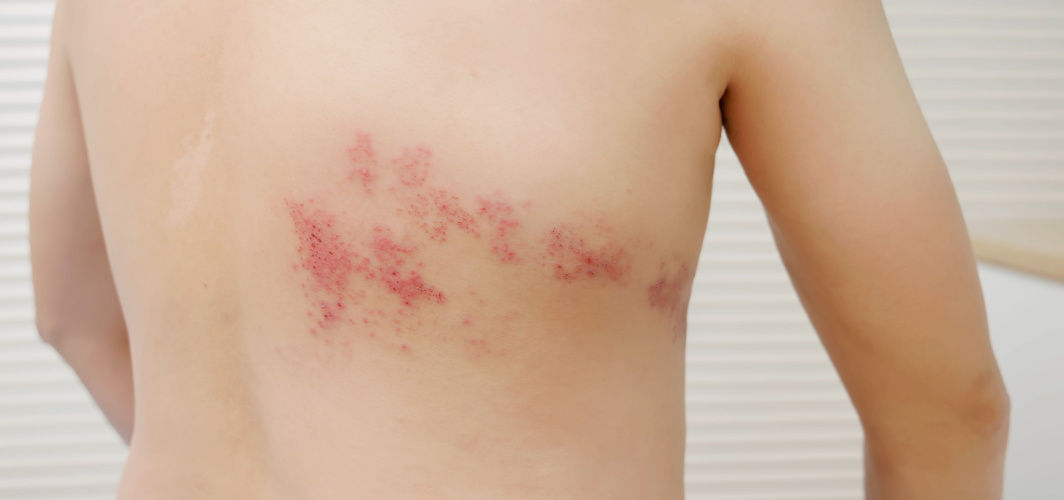
Many of us have had chickenpox at least once in our lives. However, did you know that this viral condition increases your risk of developing shingles years later? Shingles is a painful condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. It typically presents as a painful rash with blisters, usually on one side of the body. Notably, it is mostly seen in people who have experienced chickenpox in the past because the virus can remain dormant in your nerve cells for years before reactivating.
Hence, it is advised to get vaccinated against this debilitating condition, especially if you're aged 50 and above. One of the most effective vaccines available for preventing shingles is Shingrix. Approved by leading health authorities, including the World Health Organization (WHO), Shingrix has shown high efficacy in preventing shingles and its complications. In this blog, we will delve into comprehensive insights about the vaccines against shingles and their potency.
What is Shingrix?
Shingrix is a vaccine developed to prevent shingles, a painful rash caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. It is a non-live, recombinant vaccine that contains a protein found in the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
A recombinant vaccine is created by combining genes from a pathogen (in this case VZV) with the genes of another organism (often a harmless virus or bacteria), which then stimulates the immune system without causing the disease.
The vaccine is administered in two doses, with a recommended interval of two to six months between doses.
How Does Shingrix Work?
Shingrix works by stimulating the immune system to produce a strong response against the varicella-zoster virus. It helps the immune system recognise and respond quickly to the virus, preventing it from reactivating and causing shingles.
The vaccine's efficacy has been shown to be over 90% in preventing shingles in individuals aged 50 years and older.
Is Shingrix Better than Other Shingles Vaccines?
Shingrix is the preferred vaccine for preventing shingles, as recommended by the public health agency of the USA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Furthermore, it is more effective than the previous shingles vaccine, Zostavax, and provides longer-lasting protection. Unlike Zostavax, Shingrix can be given to individuals who have previously received Zostavax or had shingles.
Who Should Get the Shingrix Vaccine?
Things to be kept in mind before going for the Shingrix vaccine include:
1. Age recommendations
- The Shingrix vaccine is recommended for adults aged 50 years and older.
- Even if you have had shingles in the past, it is still recommended to get vaccinated as the virus can reactivate.
2. Individuals with certain medical conditions
- If you have a weakened immune system due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS, cancer or any other immunocompromising condition, it is important to consult your doctor about getting the vaccine.
- Individuals who are receiving immunosuppressive therapy or have had an organ transplant may also be eligible for the vaccine. However, they must consult their doctor before taking the vaccine.
3. Considerations for pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers
- The safety of the Shingrix vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established. Hence it is not recommended during this time.
- If you are planning pregnancy, it is recommended to complete the vaccination series before conceiving.
4. Considerations for those with chronic conditions
- Individuals with chronic conditions such as diabetes or heart disease can safely receive the Shingrix vaccine after consulting with their healthcare provider.
Effectiveness and Safety of Shingrix
Shingrix has undergone extensive clinical trials to determine its effectiveness and safety. In clinical trials, Shingrix has shown to be highly effective in preventing shingles and its complications.
The vaccine has been found to reduce the risk of shingles by more than 90% in various age groups. Moreover, it has also been found to be effective in preventing postherpetic neuralgia, which otherwise causes long-lasting pain even after the disappearance of the rash.
Shingrix can cause some side effects, though they are usually mild and temporary. Some common side effects of Shingrix include:
- Redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Headache
These side effects typically resolve within a few days without any specific treatment. However, some extremely rare but serious side effects of Shingrix are difficulty breathing & swelling of the face or throat. Though rare, these side effects would require immediate medical attention.
How to Get the Shingrix Vaccine?
The Shingrix vaccine, developed by GlaxoSmithKline, is now available in India. It has been approved by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) and is widely accessible in pharmacies and healthcare clinics across the country.
The Shingrix vaccine is administered as a two-dose series, with the second dose given 2 to 6 months after the first dose. This two-dose regimen provides strong protection against shingles and its complications, even in individuals who have previously had shingles or received the older Zostavax vaccine.
Preparing for the Shingrix Vaccine
Before taking the medication, your doctor will assess you for any underlying health conditions, ongoing treatments, or medications you are taking. It further includes reviewing your past allergic reactions, vaccinations, and previous exposure to chickenpox or shingles.
This is necessary to determine if you have any conditions or factors that may affect the vaccine's effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
What to Expect After Vaccination?
While most individuals do not experience any significant side effects, some might experience mild reactions. Here's what you need to know:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site: Applying a cool compress and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
- Fatigue or muscle pain: Resting, staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage these symptoms.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help relieve headaches.
- Fever: Dressing lightly, drinking plenty of fluids, and using over-the-counter antipyretics can help lower the temperature.
Booster Dose of Shingrix Vaccine
The Shingrix vaccine provides long-lasting protection against shingles. Studies have shown that its effectiveness remains high for at least four years after vaccination.
As of now, there are no official recommendations for booster doses. However, ongoing research is being conducted to determine if additional doses will be needed in the future.
Benefits of Getting Vaccinated Against Shingles
The benefits of getting vaccinated against shingles include:
1. Provides protection against shingles-related pain, rash, blisters and other complications such as vision loss, nerve damage, and bacterial skin infections.
2. Reduces the risk of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), which is a common complication of shingles characterised by persistent nerve pain even after the rash has healed. Shingrix has been shown to reduce the risk of developing PHN by more than 90%.
3. By getting vaccinated, you not only protect yourself from shingles but also contribute to herd immunity, thereby limiting the spread of the virus and protecting vulnerable populations who cannot receive the vaccine.
Takeaway
Getting vaccinated against shingles with Shingrix can significantly reduce your risk of developing this painful condition. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the benefits and potential side effects of the vaccine. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and protecting yourself against shingles is an important step in maintaining your health and well-being.
For more information on shingles or Shingrix,
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Do I have to stop my medication before getting Shingrix?
There are no known interactions between the Shingrix vaccine and other medications. It is safe to receive the vaccine even if you are taking prescription medications.
Q. How effective is Shingrix?
Shingrix is highly effective in preventing shingles and its complications. Clinical trials have shown that it reduces the risk of developing shingles by more than 90% in people aged 50 years and older. It also reduces the severity and duration of pain if shingles do occur.
Q. Are there any side effects of Shingrix?
Like any vaccine, Shingrix may cause temporary side effects such as pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, as well as muscle pain, fatigue, and headache. These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own within a few days.
Q. How many doses of the Shingrix vaccine are needed?
The Shingrix vaccine is given in two doses, with a recommended interval of two to six months between doses. Both doses are necessary to ensure optimal protection against shingles.
Q. Who should get the Shingrix vaccine?
The Shingrix vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 and above, including those who have previously had shingles or received the older shingles vaccine. It is especially important for individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic medical conditions.
Q. Can Shingrix give you shingles?
The Shingrix vaccine is made from a part of the dead virus that cannot cause shingles.
General Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

General Health
Simple Carbohydrates vs. Complex Carbohydrates: Knowing the Difference
Explore the contrast between simple and complex carbohydrates. Enhance your nutritional awareness for a balanced diet and better health.
General Health
Most Googled Questions On Kidney Stones Answered By An Apollo Expert
Should you be drinking beer if you have kidney stones? Read on to know the answers to ten such questions associated with kidney stones, kidney stones symptoms and kidney stones treatment.

General Health
How Does Chemotherapy Work?
The rapidly dividing cancerous cells outnumber healthy ones at a devastating rate. Chemotherapy is one such treatment modality that stops this lethal multiplication, besides radiation and surgery. Read along to know the role of chemotherapy in cancer treatment.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Science-backed Home Remedies for Burns and Blisters
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

General Health
Simple Carbohydrates vs. Complex Carbohydrates: Knowing the Difference
Explore the contrast between simple and complex carbohydrates. Enhance your nutritional awareness for a balanced diet and better health.

General Health
Most Googled Questions On Kidney Stones Answered By An Apollo Expert
Should you be drinking beer if you have kidney stones? Read on to know the answers to ten such questions associated with kidney stones, kidney stones symptoms and kidney stones treatment.

General Health
How Does Chemotherapy Work?
The rapidly dividing cancerous cells outnumber healthy ones at a devastating rate. Chemotherapy is one such treatment modality that stops this lethal multiplication, besides radiation and surgery. Read along to know the role of chemotherapy in cancer treatment.