Diabetes Management
What is prediabetes and can it be reversed?
4 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 04 November 2020, Updated on - 30 August 2023
Share this article
0
1 like

What is prediabetes?
What are the signs and symptoms of prediabetes?
What causes prediabetes?
Researchers are not sure of the exact cause for the insulin regulation process to become impaired. A few contributing factors include:
- Being overweight and having excess fat around the abdomen increases the risk for prediabetes because the extra fat tissue can make the body more insulin resistant. A large waist size of more than 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women is linked to insulin resistance.
- Lack of physical activity increases the risk of prediabetes. Being active helps manage weight, improves glucose control, and helps in utilizing insulin more effectively.
- The risk of prediabetes increases if there is a history of type 2 diabetes in the family (parent or sibling).
- Though diabetes can occur at any age, the risk of developing prediabetes increase after 45 years of age.
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) increases the risk of developing prediabetes for the mother. It also increases the child’s future diabetes risk.
- People with polycystic ovary syndrome, a condition characterized by obesity, irregular menstruation cycles, and excessive hair growth in women, have a higher risk of prediabetes.
- Sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea increase the risk of prediabetes.
- Smoking can be a factor that causes prediabetes, as nicotine is linked to increased insulin resistance.
Additionally, when health problems like high blood pressure, low HDL (good) cholesterol, and high triglycerides (a type of fat) occur along with obesity, they are associated with insulin resistance, which can trigger prediabetes.
Can prediabetes be reversed?
How can prediabetes be reversed?
- Reducing weight – Even a modest weight loss of about 5% to 7% can significantly improve blood glucose control and reverse prediabetes.
- Increasing physical activity – Moderate activity of at least 150 minutes per week, which is 30 minutes for 5 days a week, is recommended to keep type 2 diabetes at bay.
- Consuming a healthy diet - A diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats; and eating regularly scheduled meals throughout the day can also prevent type 2 diabetes.
- Reducing stress
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol intake
Conclusion
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Aerobic or Resistance Exercises: Which One is Ideal to Manage Blood Sugar?
The American Diabetes Association recommends a combination of aerobic exercises like brisk walking or cycling (at least 150 minutes per week) and resistance training like weightlifting (2-3 sessions per week) for people with diabetes. Aerobic exercises help lower blood sugar by using glucose for energy and improving insulin sensitivity, while resistance exercises improve muscle strength and promote glucose uptake, aiding in blood sugar control.
Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Pass On To Generations?
Not only family history, there are other factors that can increase the risk of diabetes. These factors include being 45 years or older, a sedentary lifestyle, being obese or overweight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, gestational diabetes, PCOS, stress and depression, and a history of heart disease. Individuals with two or more risk factors have a higher likelihood of developing diabetes compared to others.
Diabetes Management
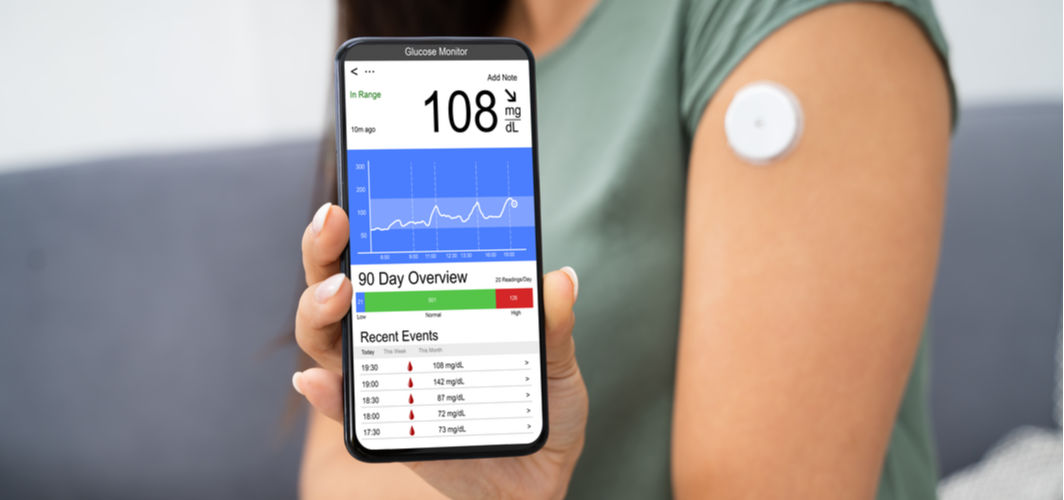
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Aerobic or Resistance Exercises: Which One is Ideal to Manage Blood Sugar?
The American Diabetes Association recommends a combination of aerobic exercises like brisk walking or cycling (at least 150 minutes per week) and resistance training like weightlifting (2-3 sessions per week) for people with diabetes. Aerobic exercises help lower blood sugar by using glucose for energy and improving insulin sensitivity, while resistance exercises improve muscle strength and promote glucose uptake, aiding in blood sugar control.

Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Pass On To Generations?
Not only family history, there are other factors that can increase the risk of diabetes. These factors include being 45 years or older, a sedentary lifestyle, being obese or overweight, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, gestational diabetes, PCOS, stress and depression, and a history of heart disease. Individuals with two or more risk factors have a higher likelihood of developing diabetes compared to others.

Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: How Does it Help?
CGM is a device that helps individuals with diabetes track their glucose levels continuously. A tiny sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid. It helps individuals monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night, thereby allowing them to improve their HbA1c levels, reduce hypoglycemia events, and assess the impact of diet and exercise on glucose levels.