Digestive Health
Suffering Frequent Acidic Burps? Get Checked For These Digestive issues
3 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 27 April 2022, Updated on - 21 August 2023
Share this article
0
3 likes
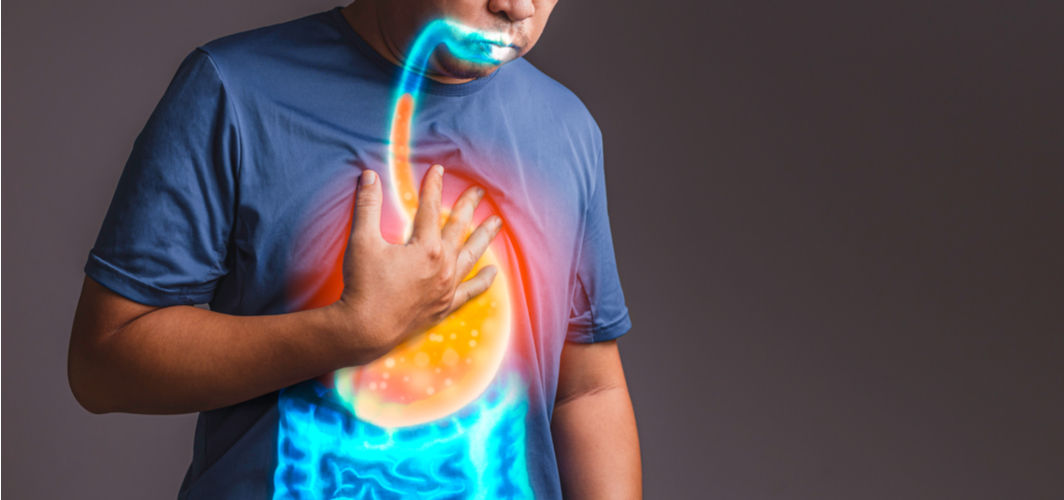
Most of us experience belching (acidic burp) occasionally, especially after having a heavy meal. However, if the frequency of belching increases unusually, it could be an indication of acid reflux or Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). While both the conditions share the same primary symptom, gastric reflux, they are quite different from each other. The article explains both acid reflux and GERD in detail below.
Acid Reflux vs GERD
Acid reflux is a condition that occurs when the stomach acid moves backwards into the oesophagus (the tube that connects the throat to the stomach). The condition is characterised by discomfort or a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn).
However, if this discomfort occurs more than twice a week for several weeks and requires you to take antacids or medications, then you may have developed GERD. The condition is a chronic and severe form of acid reflux that causes inflammation in the lining of the oesophagus.
Cause
Acid Reflux: Acid reflux is caused by the weakening of the lower oesophagal sphincter (LES), a circular muscle valve that connects the food pipe (oesophagus) to the stomach. In a healthy individual, the valve closes once the food passes from the food pipe to the stomach. However, when the muscle doesn’t close properly, the acid produced by the stomach moves backwards into the food pipe, resulting in acid reflux.
GERD: While weakening or abnormal functioning of the LES results in GERD, factors that may increase the risk include:
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Alcohol intake
- Hiatal hernia (Bulging up of the stomach into the diaphragm)
- Connective tissue disorders, such as scleroderma
- Delayed emptying of the stomach
- Long-term use of antihistamines, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and antidepressants
Symptoms
Acid Reflux: The symptoms of acid reflux include:
- Cough
- Soreness in throat
- Bitter or metallic taste at the back of the throat
GERD: While most of the symptoms of GERD are similar to those of acid reflux, people with severe GERD may experience:
- Chest pain
- Bad breath
- Chronic dry cough
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Regurgitation of food
- A sensation of a lump in the throat
- Damage to tooth enamel
- Laryngitis
- New or worsening asthma
- Poor sleep
Treatment
We often use over-the-counter available antacids to help relieve acid reflux. However, chronic inflammation caused by GERD may require precise medical treatment or else it may damage the lining of the oesophagus severely over time. Untreated GERD may result in:
- Oesophageal stricture (narrowing of the oesophagus),
- Oesophageal ulcers (open sores in the oesophagus), and
- Barrett's oesophagus (precancerous changes to the cells of the oesophagus)
Preventive measures
Certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of acid reflux as well as GERD symptoms. Some of these lifestyle changes include:
- Maintain healthy body weight by exercising regularly
- Avoid intake of heavy, processed and fatty foods
- Choose smaller portions at mealtime
- Chew your food properly before swallowing
- Avoid going to bed immediately after a meal
- Reduce consumption of citrus fruits and juices
- Avoid caffeinated and alcoholic beverages
- Quit smoking
- Wear loose-fitting clothes
- When sleeping, elevate the head of the bed 6 to 8 inches.
Acid reflux can be managed or reduced effectively by making certain healthy lifestyle changes. However, those experiencing heartburn more than twice a week could be suffering from GERD, which if not treated can cause severe complications. Also, people with severe symptoms should consult their physician to know more about possible treatment options.
Digestive Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Digestive Health
Loose Motion: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diet & Complications
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options for loose motion or diarrhoea. It also covers potential complications and prevention measures.

Digestive Health
Probiotics Vs Prebiotics: Which Is The Better Food For Your Gut?
Probiotics and prebiotics play a key role in maintaining and improving gut health. Read to know the benefits of these gut foods in detail.

Digestive Health
Laser Treatment for Piles: Everything You Need To Know
Discover how laser treatment is transforming the management of piles, offering a less invasive and more effective solution without the need for surgery.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Hidden Health Benefits in a Bowl of Salad
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Digestive Health
Loose Motion: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diet & Complications
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options for loose motion or diarrhoea. It also covers potential complications and prevention measures.

Digestive Health
Probiotics Vs Prebiotics: Which Is The Better Food For Your Gut?
Probiotics and prebiotics play a key role in maintaining and improving gut health. Read to know the benefits of these gut foods in detail.

Digestive Health
Laser Treatment for Piles: Everything You Need To Know
Discover how laser treatment is transforming the management of piles, offering a less invasive and more effective solution without the need for surgery.