Diabetes Management
Can Diabetes Worsen Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
2 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 11 September 2023, Updated on - 14 September 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
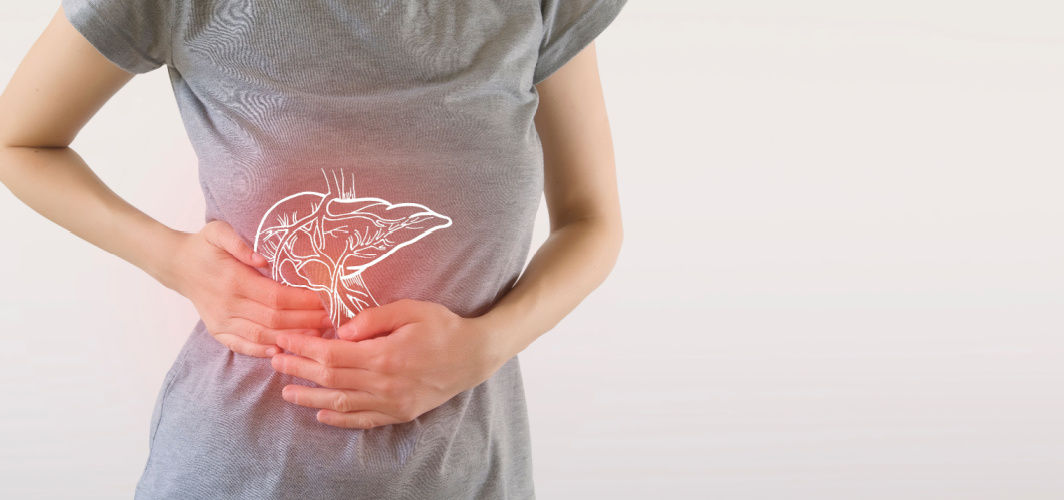
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent liver condition marked by excess fat accumulation, unrelated to alcohol consumption. It's widely known that diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, elevates the risk of NAFLD. In this blog, we'll explore the link between diabetes and NAFLD, and the mechanisms behind this connection.
What is NAFLD?
NAFLD includes various liver problems, ranging from a basic condition of having extra fat in the liver (steatosis) to a more serious one called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). While its exact cause isn’t fully understood, several risk factors include
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Diabetes
What is the Connection between Diabetes and NAFLD
Diabetes can exacerbate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) by increasing the risk of liver inflammation and other complications.
1. Insulin Resistance: Diabetes and NAFLD are closely linked due to insulin resistance. In Type 2 diabetes, cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance also affects the liver, causing increased glucose production and fat storage.
2. Inflammation: Diabetes is associated with chronic inflammation. Inflammatory processes can exacerbate NAFLD, promoting the progression from simple fatty liver to NASH, a more severe form of the disease. Inflammation worsens liver damage and may lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
3. Lipid Metabolism: Both diabetes and NAFLD involve abnormal lipid metabolism. Elevated free fatty acids in diabetes contribute to liver fat accumulation. This excess fat triggers inflammation and oxidative stress, worsening NAFLD.
4. Obesity: Obesity is a major risk factor for both Type 2 diabetes and NAFLD. These conditions often coexist, creating a cycle where each condition exacerbates the other.
Preventing and Managing the Risk
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Diabetics can reduce their NAFLD risk by managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and prescribed medication. Weight loss is particularly effective in improving liver health.
2. Monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and function can detect NAFLD early, allowing timely intervention.
3. Medications: Some medications may be prescribed to manage NAFLD in diabetic patients, but lifestyle changes are fundamental to treatment.
Conclusion
The diabetes-NAFLD connection involves complex factors, including insulin resistance, inflammation, and abnormal lipid metabolism. Diabetics should be aware of their heightened NAFLD risk and take proactive steps to manage it. By controlling blood sugar levels, embracing a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of NAFLD thereby safeguarding their liver.
Diabetes Management
Consult Top Diabetologists
View AllLeave Comment
Recommended for you
Diabetes Management
Diabetic Foot: Can it be Prevented?
The development of diabetic foot can be prevented through various measures. Effective prevention includes regular foot care, such as daily inspection and cleaning, wearing comfortable and proper-fitting shoes, managing blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and seeking immediate medical attention for any foot issues.

Diabetes Management
Are Low-carb Diets Healthy?
A low-carb diet is characterised by the reduced intake of carbohydrates and increased consumption of protein and healthier fats. Most low-carb diets limit carbohydrates to less than 130g per day. Scientific evidence indicates that low-carb diets can positively impact health indicators such as triglycerides, cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, leading to their popularity and adoption for several decades.
Diabetes Management
Best Exercises For Diabetes Prevention
Regular exercise is essential for managing and preventing type 2 diabetes. It improves blood glucose control, aids in weight management, and addresses common health issues in older adults. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program. Read on to learn more about how exercise can benefit diabetics.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Diabetic Foot: Can it be Prevented?
The development of diabetic foot can be prevented through various measures. Effective prevention includes regular foot care, such as daily inspection and cleaning, wearing comfortable and proper-fitting shoes, managing blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption, and seeking immediate medical attention for any foot issues.

Diabetes Management
Are Low-carb Diets Healthy?
A low-carb diet is characterised by the reduced intake of carbohydrates and increased consumption of protein and healthier fats. Most low-carb diets limit carbohydrates to less than 130g per day. Scientific evidence indicates that low-carb diets can positively impact health indicators such as triglycerides, cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, leading to their popularity and adoption for several decades.

Diabetes Management
Best Exercises For Diabetes Prevention
Regular exercise is essential for managing and preventing type 2 diabetes. It improves blood glucose control, aids in weight management, and addresses common health issues in older adults. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program. Read on to learn more about how exercise can benefit diabetics.