Digestive Health
Gallbladder Stones: Know The Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
5 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 16 March 2023, Updated on - 21 June 2023
Share this article
0
0 like
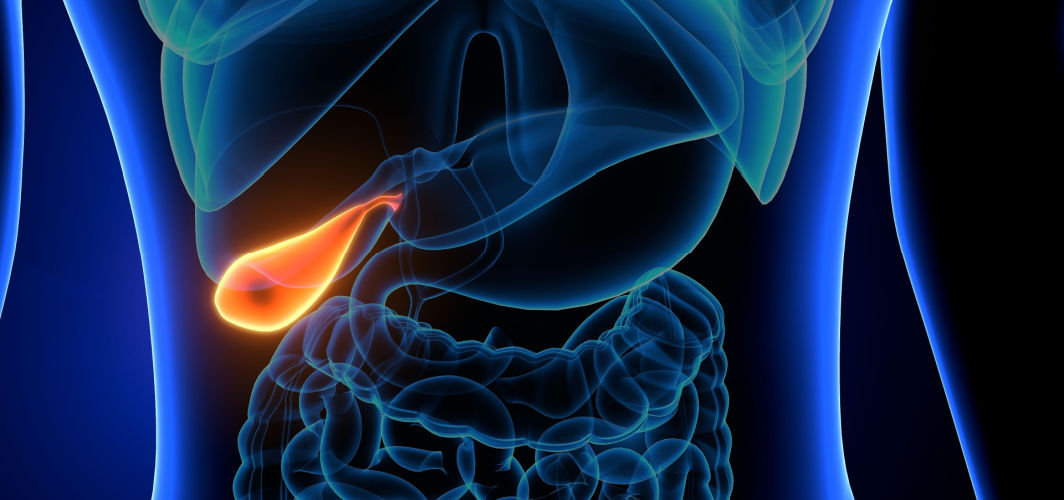
It's quite astonishing to know that gallbladder stones are one of the most commonly occurring disorders in the world. Recent research has shown gallbladder stones to be affecting 10-15% of the world's population. In India alone, approximately 4% of the population is diagnosed with gallstones. These stats are enough to make us understand the fact that the risk of contracting this medical condition is pretty high and it mostly affects people over 40 years of age. Therefore, it calls for action.
But before we actually nose dive into its prevention and treatment, let's first understand what are gallstones, and the causal factors behind their formation.
Gallstones & Their Types
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ, located just beneath the liver. It stores and releases the digestive fluid bile that helps in digesting fats. Gallstones of cholelithiasis are nothing but hardened stone-like deposits made from the digestive fluid in the gallbladder. These stones form when there's too much cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile or when the gallbladder fails to empty itself properly.
Gallstones or cholelithiasis are mainly of three kinds.
- Cholesterol stones: As the name suggests, these are usually made of hardened cholesterol. They are mostly yellowish-green in colour. Excess cholesterol in your body makes up about 75% of gallstones. These stones can grow big and block bile ducts.
- Pigment stones: Made of bilirubin, these gallstones are usually dark in colour. These gallstones are usually small in size but are found in more numbers inside the gallbladder.
- Mixed stones: This is the most common type of gallstone. Made up of cholesterol and salts, they develop in batches in the body.
Gallbladder Stones Symptoms
In most cases, the presence of gallstones shows no symptoms or signs. However, sometimes if these stones block a duct, the symptoms may include:
- Sudden and intensifying abdominal pain
- Bloating or distention
- Back pain between shoulder blades
- Pain in your right shoulder
- Heartburn after meals
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever and chills
Gallstone pain occurs in episodes and may last from several minutes to a few hours.
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Gallstones can be diagnosed by,
- Physical examination by medical professionals
- Abdominal ultrasound - One of the most commonly used tests
- Endoscopic examination – Used to identify smaller stones that may have been missed by an abdominal ultrasound
- Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan – An imaging test to diagnose liver, gallbladder and bile ducts disorders
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) – A form of MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan
- Computerized tomography (CT) Scan - Uses a series of X-rays taken from different angles to diagnose the size and location of stones
- Blood tests - For diagnosing infection, pancreatitis, jaundice or complications from gallstones
Treatment for Gallstones
The treatment for gallbladder stones depends on the position and size of the gallstones. In most cases, medication or dietary modifications can eliminate gallstones. However, in some cases, gallbladder surgery might be required.
- Dietary modifications – These call for reducing or eliminating dairy products and fatty foods from the diet.
- Medications – In some patients, medicines help dissolve gallstones. However, this process takes time. This option is mostly reserved for patients who can't undergo surgery.
- Lithotripsy – In this process, sound waves are used to disintegrate the gallstones. This treatment is used for small and soft gallstones.
- Surgery - If the gallstones frequently recur, doctors might advise surgery, which is the removal of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder is not a vital organ of the body and post gallbladder surgery, the body functioning is not affected. Different types of surgery can be used to remove the stone.
Types of Gallbladder Surgery
- Endoscopy: This procedure does not require any cuts or incisions. A long tube is inserted through the throat to remove the gallstones. In this procedure, the gallbladder is not removed; only the stone is removed.
- Laparoscopy: This process uses small keyhole incisions in the abdomen through which a small camera is inserted. One keyhole is used to insert the camera and another to remove the gallbladder. This procedure makes recovery faster.
- Open surgery: People with complicated conditions may require open surgery. This requires a longer hospital stay and a longer recovery period.
To sum it up, gallstones are very common and most people may never feel any gallbladder stones symptoms. Only when these stones begin to move, do they get into delicate spaces like ducts and become dangerous. However, there are many treatment options available. Only in severe cases, an individual may need to undergo gallbladder surgery.
Consult Apollo's Expert Surgeons
FAQs
1. Can gallstones be treated without surgery?
Yes, gallstones can be treated without surgery. There are medicines that can help dissolve the stones but it may take many years for the stones to dissolve. Using extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), doctors try to break the stones into smaller sizes.
2. What is a gallbladder attack?
A gallbladder attack is sudden and severe pain in the upper right abdomen and can often be triggered after having a fatty meal.
3. If left untreated, can gallstones cause infection?
Yes. If left untreated, gallstones can get bigger and lead to complications like jaundice, pancreatitis, etc.
4. Are gallstones a serious medical condition?
In most cases, gallstones themselves are not serious and people have zero symptoms. However, in rare cases, they can lead to serious health issues.
5. Can gallstones be prevented?
Yes, gallstones can be prevented by having a high-fibre diet which is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates. Regular physical activity is also important.
Consult Apollo's Expert Surgeons
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Digestive Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Digestive Health
Regular Use Of Laxatives Can Increase Your Risk Of This Brain Disease By 50%
According to several researchers, regular use of laxatives can increase the risk of dementia by more than 50%. Laxatives can reduce the barrier function of our brain which can lead to a stroke, a known risk factor for dementia. Hence, it is advised not to use off-the-counter laxatives without consulting a gastroenterologist.

Digestive Health
Constipation Treatment: Best Herbal Supplements That Can Bring Relief
Constipation is not only painful but can also affect your daily life. Read to know easy remedies for constipation and natural pills for constipation treatment.

Digestive Health
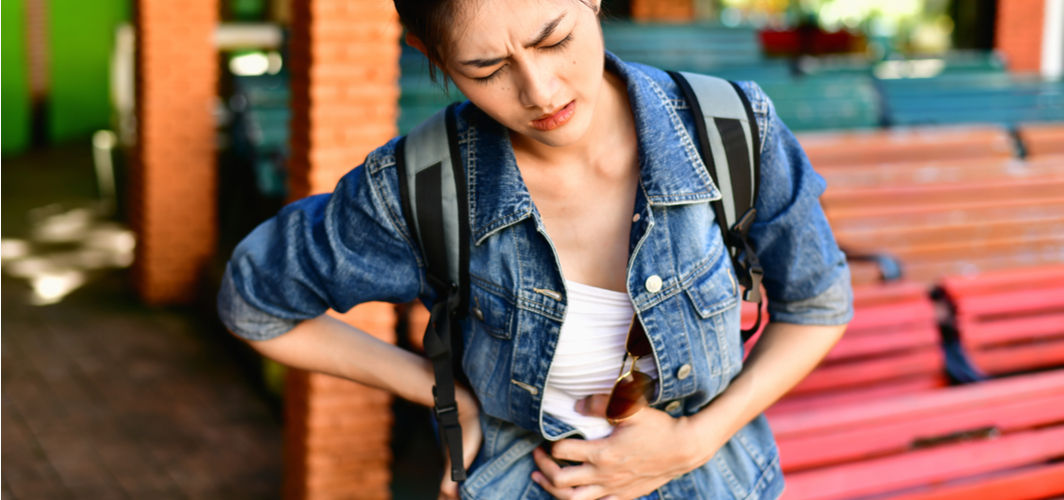
How to Identify Abdominal Pain Caused by Gallstones
Sudden, severe pain in the upper right abdomen, fever, or yellow skin, could indicate the presence of gallstones. These stones are usually made up of cholesterol and develop in the gallbladder.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Hidden Health Benefits in a Bowl of Salad
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Digestive Health
Regular Use Of Laxatives Can Increase Your Risk Of This Brain Disease By 50%
According to several researchers, regular use of laxatives can increase the risk of dementia by more than 50%. Laxatives can reduce the barrier function of our brain which can lead to a stroke, a known risk factor for dementia. Hence, it is advised not to use off-the-counter laxatives without consulting a gastroenterologist.

Digestive Health
Constipation Treatment: Best Herbal Supplements That Can Bring Relief
Constipation is not only painful but can also affect your daily life. Read to know easy remedies for constipation and natural pills for constipation treatment.

Digestive Health
How to Identify Abdominal Pain Caused by Gallstones
Sudden, severe pain in the upper right abdomen, fever, or yellow skin, could indicate the presence of gallstones. These stones are usually made up of cholesterol and develop in the gallbladder.
