Digestive Health
How Probiotics Keep the Digestive System in Great Shape
4 min read
By Apollo 24/7, Published on - 09 March 2021, Updated on - 18 October 2022
Share this article
1
26 likes
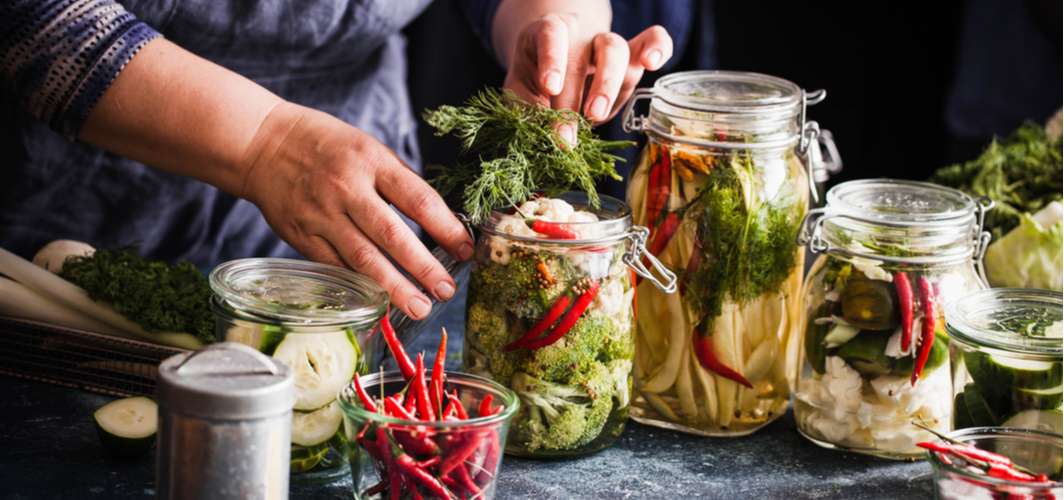

Probiotics are live microorganisms (bacteria and yeasts) similar to the ones that are present in the digestive tract. The beneficial effects of probiotics are attributed to improving intestinal health, enhancing immune response, reducing serum cholesterol, and preventing cancer. Probiotics can be introduced into the body through traditional foods or dietary supplements. Research proves that probiotics help maintain a healthy and properly functioning digestive system that filters out and eliminates harmful microbes, chemicals, toxins, and waste products. Probiotics are also increasingly known for their ability to prevent and/or treat gastrointestinal disorders.
Role of probiotics in digestive health
The gut is home to around 100 trillion microorganisms, both good and bad. The composition and functions of these microorganisms that include bacteria, yeast, and fungi play a major role in maintaining one’s health. The good microbes of the gut are required for carrying out metabolic, digestive, and immune functions. Probiotics are foods or supplements that contain beneficial (friendly, good, or healthy) bacteria or yeast that help to restore the composition of gut microorganisms and their beneficial functions.
Probiotics play a vital role in digestive health, and they help to:
- Promote a healthy digestive system.
- Help the body in digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Help in the synthesis of vitamins and activation of some enzymes required for digestion.
- Help to maintain a healthy microbiota (community of microorganisms) in the digestive tract.
- Restore the natural balance of gut microbiota after being disturbed by infection, illness, improper diet, or antibiotic medications.
- Inhibit the growth of pathogenic or harmful microorganisms in the gut and prevent bacterial or fungal infections.
Other important benefits of probiotics include:
- Help the liver to neutralize and eliminate toxins from the body.
- Influence the body’s immune response like inflammation and allergies.
Digestive issues that are benefited from probiotics
- Diarrhoea: Probiotics can help slow down the contractions of the gastrointestinal tract to stop diarrhoea.
- Constipation: Probiotics relieve constipation by decreasing the transit time (time taken for the food to move through the digestive tract), resulting in lesser reabsorption of water making the stools softer and easier to pass.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Probiotics help ease the symptoms of IBS that include abdominal pain, bloating, cramping, gas, constipation and/or diarrhoea.
- Lactose intolerance: Probiotics are known to alleviate the symptoms of lactose intolerance (inability to digest lactose in milk and milk products) that causes abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhoea.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Probiotics can help treat IBD by modulating the intestinal microflora from inflammatory to anti-inflammatory.
- During and after antibiotic therapy: Probiotics help relieve antibiotic-related symptoms like diarrhoea. Antibiotics alter the gut microbiota by killing the good bacteria and cause diarrhoea. Diarrhoea can also result from a bacterial infection in the large intestine by the bacterium Clostridium difficile due to the use of antibiotics.
What are the common types of probiotics?
Probiotics may contain a variety of microorganisms. Different types of probiotics exert different health effects, but they mostly contain bacteria or yeast. The most common types are:
- Bacteria - genus Lactobacillus and genus Bifidobacterium (there are various species within each genus, for example - Lactobacillus acidophilus)
- Yeast - Saccharomyces boulardii
Sources of probiotics
One can increase the amount of probiotics in the body through foods, drinks, and dietary supplements.
Foods: Fermented foods are rich sources of natural probiotics that benefit the digestive system. These include dairy products such as fermented milk, milk powder, buttermilk, ice cream, yogurt, and cheese. Commonly consumed daily foods like idli, dosa and dhokla are also fermented and healthy. Non-dairy food products include pickles, nutrition bars, cereals, soy-based products, and juices.
Dietary supplements: Probiotic supplements are another way of adding good bacteria to the body. These are available in different forms and include:
- Foods and drinks
- Capsules or pills
- Liquids
- Powders
Probiotic supplements are usually taken in combination with ‘prebiotics’. Prebiotics are food sources consisting of complex carbohydrates that feed the beneficial microbes in the gut thereby helping them flourish.
Conclusion
The key to a healthy microbiota is nourishing a balance among the different species of bacteria in the gut. Probiotic foods and supplements can be a safe way to increase the number of healthy bacteria and keep the gut microbiota balanced. Probiotics help improve the digestive ability and build strong immunity against diseases and problems related to the digestive system. A healthy digestive health in turn leads to a healthy immune system and good mental health.
Talk to a gastroenterologist if you have any questions related to digestive health.
You can also explore our range of probiotics to boost your digestive health.
Digestive Health
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
Digestive Health
बवासीर को घर पर ही प्राकृतिक तरीके से ठीक कैसे करें
बवासीर को का अर्थ होता है गुदाद्वार या फिर निचले मलाशय में नसों में सूजन और जलन का हो जाना। मलत्याग करते समय व्यक्ति के मलाशय से रक्तस्राव एवं दर्द होता है। जानिए इस बीमारी के बारे मे।

Digestive Health
Laser Treatment for Piles: Everything You Need To Know
Discover how laser treatment is transforming the management of piles, offering a less invasive and more effective solution without the need for surgery.

Digestive Health
Crohn’s Disease: A Lifelong Form of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
A person experiencing abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhoea, weight loss, and rectal bleeding over prolonged periods could be affected by Crohn’s disease.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

Hidden Health Benefits in a Bowl of Salad
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Digestive Health
बवासीर को घर पर ही प्राकृतिक तरीके से ठीक कैसे करें
बवासीर को का अर्थ होता है गुदाद्वार या फिर निचले मलाशय में नसों में सूजन और जलन का हो जाना। मलत्याग करते समय व्यक्ति के मलाशय से रक्तस्राव एवं दर्द होता है। जानिए इस बीमारी के बारे मे।

Digestive Health
Laser Treatment for Piles: Everything You Need To Know
Discover how laser treatment is transforming the management of piles, offering a less invasive and more effective solution without the need for surgery.

Digestive Health
Crohn’s Disease: A Lifelong Form of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
A person experiencing abdominal pain, cramps, diarrhoea, weight loss, and rectal bleeding over prolonged periods could be affected by Crohn’s disease.