Diabetes Management
Why Should Diabetics Regularly Monitor Their Blood Glucose?
4 min read
By Apollo 24|7, Published on - 13 March 2023, Updated on - 20 June 2023
Share this article
0
1 like
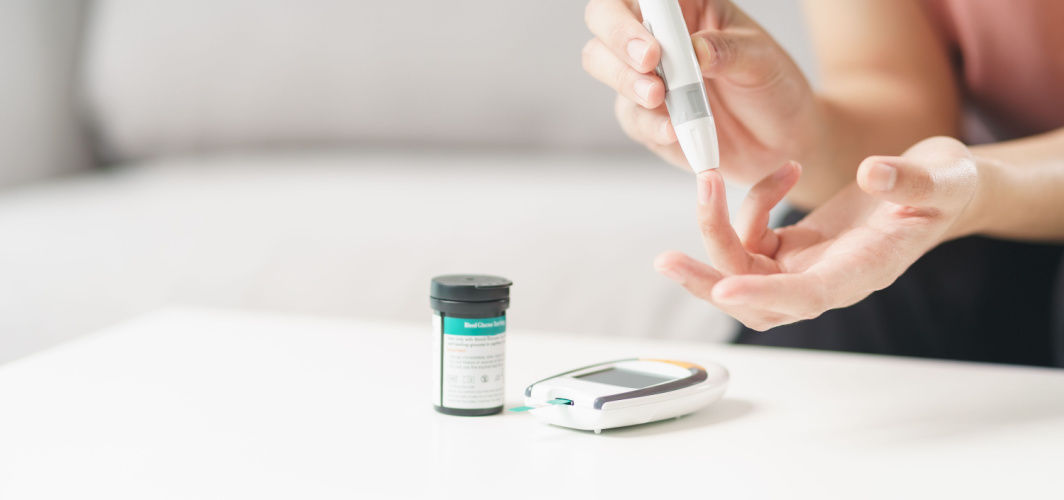
Monitoring blood sugar levels periodically is one of the most essential aspects of managing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This practice enables you to identify the food or lifestyle-related triggers that may cause your blood sugar levels to rise or drop significantly. Using this information, your doctor can create the best possible diabetes care plan for you. In most cases, the doctors educate the patients on how often they need to check their glucose levels. This is where diabetic monitors and blood sugar meters come in handy. These monitors allow the patients to record their blood sugar levels at all times. Here are other benefits of using diabetic monitors.
Benefits Of Using A Diabetic Monitor
Following are some of the major benefits of using a diabetic monitor:
1. Monitoring your blood sugar levels help you figure out whether or not you are meeting your glucose targets. This can help avoid long-term diabetes-related complications and keep the unpleasant symptoms of low and high blood sugar at bay. This information helps you determine the best way of managing your diabetes on a day-to-day basis.
2. For diabetics, monitoring their blood sugar levels is vital to determine just how well their existing treatment plan is working and whether or not it needs any modification. The information gathered by using a diabetic monitor can help your doctor formulate the best treatment plan for you. These decisions can prove to be extremely helpful in delaying or preventing diabetes complications like stroke, heart attack, blindness, kidney disease, and even amputation.
3. Diabetes affects every individual in a different way. So, there’s no one right approach for diabetes management for everyone. Monitoring your glucose level will help you gain a better understanding of what works for you and what doesn’t, such as taking your medicine or insulin at different times, exercising and eating different foods.
How To Use A Diabetic Monitor?
There are primarily two ways for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar levels at home. These include:
1. Glucometer and finger stick
The most common and widely used blood sugar monitoring method involves the use of a glucometer and test strips. Also referred to as a finger stick check, this method requires you to prick your finger with a needle (called a lancet) to release a drop of blood. Then, you need to place this blood drop on the test strip, placed in the glucometer, which shows you the blood sugar levels within a few seconds. The limitation of this method is that it only gives you information about your blood sugar at a specific moment. So, diabetics may have to check their blood glucose many times during the day.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)
This method of blood sugar monitoring requires diabetics to wear a device that keeps a check on their glucose levels at all times. A CGM uses this data to create a graph displaying the complete picture of how your sugar levels vary over time. Most of these devices use a tiny sensor, which is inserted under your skin. This sensor measures your glucose levels 24 hours a day. There are many different brands and types of CGMs, some of which are linked to specific insulin pumps while others work independently. Most of these devices can send alerts or alarms when high or low blood sugar levels are detected.
Explore Continuous Glucose Monitor
You can choose either one or even both methods as per your needs.
Conclusion
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring can vary from person to person. However, every diabetic should keep an eye on their blood sugar levels to prevent any complications. So, all you need to do is to just follow the instructions given by your doctor and maintain a healthy lifestyle. If you need more information,
Consult Apollo's Expert Diabetologists
You can also manage your diabetes like a pro with Apollo 24|7's 12-week empower programme.
Medically reviewed by Dr Sonia Bhatt.
Diabetes Management
Leave Comment
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Understanding the Impact of Standing on Insulin Sensitivity
A new study has found that mere standing can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.

Diabetes Management
These Foods Can Increase Your Risk Of Diabetes
Nitrates and nitrites in processed foods may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. It is important to avoid foods containing nitrates and have a balanced diet that is low in refined carbohydrates, high in fibre and rich in nutrients.

Diabetes Management
Does Unexplained Weight Loss Indicate Diabetes?
Explore the fascinating link between unintentional weight loss and diabetes. Discover the truth behind weight loss as an indication of diabetes.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
Visual Stories

8 Fruits That are Incredibly Healthy for Diabetes
Tap to continue exploring
Recommended for you

Diabetes Management
Understanding the Impact of Standing on Insulin Sensitivity
A new study has found that mere standing can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.

Diabetes Management
These Foods Can Increase Your Risk Of Diabetes
Nitrates and nitrites in processed foods may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. It is important to avoid foods containing nitrates and have a balanced diet that is low in refined carbohydrates, high in fibre and rich in nutrients.

Diabetes Management
Does Unexplained Weight Loss Indicate Diabetes?
Explore the fascinating link between unintentional weight loss and diabetes. Discover the truth behind weight loss as an indication of diabetes.
